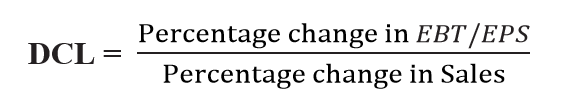Operating leverage:
Operating leverage is concerned with the relationship between the firm’s sales revenue and its earnings before interest and taxes, or EBIT (Operating profit). Operating leverage is defined as the firm’s ability to use fixed operating costs to magnify the effects of changes in sales on its earnings before interest on tax.

Degree of Operating Leverage
The degree of operating leverage may be defined as percentage change in the EBIT resulting from a percentage change in the sales. It can be calculated with the help of the following formula:
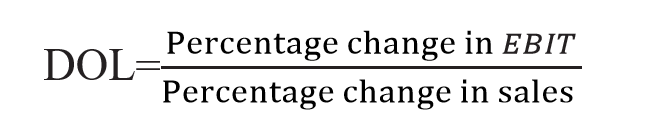
High operating leverage is risky because of the presence of high fixed operating costs. And a small change in sales causes high fluctuations in the company’s EBIT.
Financial leverage:
Financial leverage is concerned with the relationship between the firm’s EBIT and its EBT/EPS. It is defined as the firm’s ability to use fixed financial charges to magnify the effects of charge in EBIT/operating profit on the firm’s EBT and EPS.
Financial leverage is defined as “the ability of a firm to use fixed financial charges to magnify the effects of changes in EBIT on the earnings per share”. It involves the use of funds obtained at a fixed cost in the hope of increasing the return to the shareholders. Fixed financial charges include debenture and preference dividends.
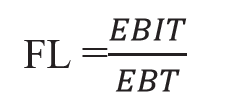
If preference share and tax are given
Then Financial leverage is calculated by taking into account preference dividend after adjusting tax. The formula will be
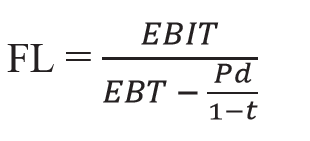
Degree of Financial Leverage:
The degree of financial leverage may be defined as the percentage change in EBT/EPS as a result of the percentage change in earnings before interest and tax (EBIT). This can be calculated by the following formula
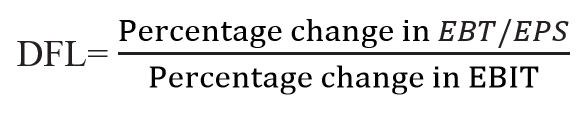
High financial leverage is risky because of the presence of high fixed financial costs. And a small change in EBIT causes high fluctuations in the company’s EBT/EPS.
COMBINED LEVERAGE
Combined/Total leverage is concerned with the relationship between the firm’s sales revenue and EBT/EPS.
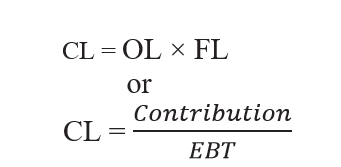
If preference share and tax is given
Then Combined leverage is calculated by taking into account preference dividend after adjusting tax. The formula will be
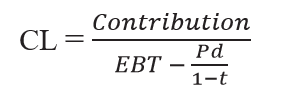
Degree of Combined Leverage:
The percentage change in firms earnings per share (EPS) results from a one per cent change in sales. This is also equal to the firm’s degree of operating leverage (DOL) times its degree of financial leverage (DFL) at a particular level of sales.